Functions and classes to support common computer vision concepts and operations. More...
Classes | |
| class | Camera::Linear |
| A linear camera with zero skew. More... | |
| class | Camera::Cubic |
| A camera with zero skew and cubic distortion. More... | |
| class | Camera::Quintic |
| A camera with zero skew and quintic distortion. More... | |
| class | Camera::Harris |
| A Camera with zero skew and Harris distortion. More... | |
| class | Camera::ArcTan |
| A Camera for lenses which attempt to maintain a constant view angle per pixel. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Harris::HarrisScore |
| Compute the corner score according to Harris. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Harris::ShiTomasiScore |
| Compute the score according to Shi-Tomasi. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Harris::PosInserter |
| Used to save corner positions from harrislike_corner_detect. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Harris::PairInserter |
| Used to save corner positions and scores from harrislike_corner_detect. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BasicGray< T, Cmp > |
| A helper class for performing basic grayscale morphology on an image. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Erode< T > |
| Class for performing greyscale erosion. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Dilate< T > |
| Class for performing greyscale dilation. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BasicGrayByte |
| A helper class for performing basic grayscale morphology on an image of bytes. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Erode< byte > |
| Class for performing greyscale erosion of bytes. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Dilate< byte > |
| Class for performing greyscale dilation of bytes. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Percentile< byte > |
| Class for performing percentile filtering of bytes. More... | |
| class | CVD::Morphology::Median< byte > |
| Class for performing percentile filtering of bytes. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BasicBinary< T > |
| Class for performing binary morphology. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BinaryErode< T > |
| Class for performing binary erosion. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BinaryDilate< T > |
| Class for performing binary dilation. More... | |
| struct | CVD::Morphology::BinaryMedian< T > |
| Class for performing binary median filtering. More... | |
| struct | CVD::multiplyBy< T > |
| a functor multiplying pixels with constant value. More... | |
Namespaces | |
| namespace | Camera |
| namespace | CVD::Morphology |
Modules | |
| Efficient Second Order Minimization (ESM) | |
Functions | |
| void | CVD::connected_components (const std::vector< ImageRef > &v, std::vector< std::vector< ImageRef > > &r) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | CVD::gaussianKernel (std::vector< T > &k, T maxval, double stddev) |
| template<class S , class T > | |
| T | CVD::scaleKernel (const std::vector< S > &k, std::vector< T > &scaled, T maxval) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CVD::convolveWithBox (const BasicImage< T > &I, BasicImage< T > &J, ImageRef hwin) |
| void | CVD::fast_nonmax (const BasicImage< byte > &im, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier, std::vector< ImageRef > &max_corners) |
| void | CVD::fast_nonmax_with_scores (const BasicImage< byte > &im, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier, std::vector< std::pair< ImageRef, int > > &max_corners) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_7 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_7 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_8 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_8 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_9 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_9 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_9_nonmax (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &max_corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_10 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_10 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_11 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_11 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_detect_12 (const BasicImage< byte > &im, std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int barrier) |
| void | CVD::fast_corner_score_12 (const SubImage< byte > &i, const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, int b, std::vector< int > &scores) |
| template<class It > | |
| void | CVD::haar1D (It from, It to) |
| template<class It > | |
| void | CVD::inv_haar1D (It from, It to) |
| template<class It > | |
| void | CVD::haar1D (It from, int size) |
| template<class It > | |
| void | CVD::inv_haar1D (It from, int size) |
| template<class It > | |
| void | CVD::haar2D (It from, const int width, const int height, int stride=-1) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CVD::haar2D (SubImage< T > &I) |
| template<class Score , class Inserter , class C , class B > | |
| void | CVD::harrislike_corner_detect (const SubImage< B > &i, C &c, unsigned int N, float blur, float sigmas, BasicImage< float > &xx, BasicImage< float > &xy, BasicImage< float > &yy) |
| template<class S , class D > | |
| void | CVD::integral_image (const SubImage< S > &in, SubImage< D > &out) |
| template<class S , class D > | |
| Image< D > | CVD::integral_image (const BasicImage< S > &from) |
| double | CVD::interpolate_extremum (double d1, double d2, double d3) |
| TooN::Vector< 2 > | CVD::interpolate_extremum (double I__1__1, double I__1_0, double I__1_1, double I_0__1, double I_0_0, double I_0_1, double I_1__1, double I_1_0, double I_1_1) |
| template<class I > | |
| TooN::Vector< 2 > | CVD::interpolate_extremum (const SubImage< I > &i, ImageRef p) |
| std::pair< TooN::Vector < 2 >, double > | CVD::interpolate_extremum_value (double I__1__1, double I__1_0, double I__1_1, double I_0__1, double I_0_0, double I_0_1, double I_1__1, double I_1_0, double I_1_1) |
| template<class I > | |
| std::pair< TooN::Vector < 2 >, double > | CVD::interpolate_extremum_value (const SubImage< I > &i, ImageRef p) |
| template<class Accumulator , class T > | |
| void | CVD::morphology (const SubImage< T > &in, const std::vector< ImageRef > &selem, const Accumulator &a_, SubImage< T > &out) |
| Image< T > | CVD::morphology (const SubImage< T > &in, const std::vector< ImageRef > &selem, const Accumulator &a_) |
| void | CVD::nonmax_suppression_strict (const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, const std::vector< int > &scores, std::vector< ImageRef > &nmax_corners) |
| void | CVD::nonmax_suppression (const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, const std::vector< int > &scores, std::vector< ImageRef > &nmax_corners) |
| void | CVD::nonmax_suppression_with_scores (const std::vector< ImageRef > &corners, const std::vector< int > &socres, std::vector< std::pair< ImageRef, int > > &max_corners) |
| template<class C > | |
| Image< TooN::Matrix< 2 > > | CVD::dense_tensor_vote_gradients (const SubImage< C > &image, double sigma, double ratio, double cutoff=0.001, unsigned int num_divs=4096) |
| template<class C > | |
| void | CVD::twoThirdsSample (const SubImage< C > &in, SubImage< C > &out) |
| template<class C > | |
| Image< C > | CVD::twoThirdsSample (const SubImage< C > &from) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CVD::halfSample (const BasicImage< T > &in, BasicImage< T > &out) |
| template<class T > | |
| Image< T > | CVD::halfSample (const BasicImage< T > &in) |
| template<class T > | |
| Image< T > | CVD::halfSample (Image< T > in, unsigned int octaves) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CVD::threshold (BasicImage< T > &im, const T &minimum, const T &hi) |
| template<class T > | |
| void | CVD::stats (const BasicImage< T > &im, T &mean, T &stddev) |
| template<class S , class T > | |
| void | CVD::gradient (const BasicImage< S > &im, BasicImage< T > &out) |
Variables | |
| const ImageRef | CVD::fast_pixel_ring [16] |
Detailed Description
Functions and classes to support common computer vision concepts and operations.
Function Documentation
| void CVD::connected_components | ( | const std::vector< ImageRef > & | v, |
| std::vector< std::vector< ImageRef > > & | r | ||
| ) |
Find the connected components of the input, using 4-way floodfill.
This is implemented as the graph based algorithm. There is no restriction on the input except that positions can not be INT_MIN or INT_MAX.
The pixels in the resulting segments are not sorted.
- Parameters:
-
v List of pixel positions r List of segments.
| T CVD::gaussianKernel | ( | std::vector< T > & | k, |
| T | maxval, | ||
| double | stddev | ||
| ) |
creates a Gaussian kernel with given maximum value and standard deviation.
All elements of the passed vector are filled up, therefore the vector defines the size of the computed kernel. The normalizing value is returned.
- Parameters:
-
k vector of T's holds the kernel values maxval the maximum value to be used stddev standard deviation of the kernel
- Returns:
- the sum of the kernel elements for normalization
Definition at line 48 of file convolution.h.
| T CVD::scaleKernel | ( | const std::vector< S > & | k, |
| std::vector< T > & | scaled, | ||
| T | maxval | ||
| ) |
scales a GaussianKernel to a different maximum value.
The new kernel is returned in scaled. The new normalizing value is returned.
- Parameters:
-
k input kernel scaled output vector to hold the resulting kernel maxval the new maximum value
- Returns:
- sum of the new kernel elements for normalization
Definition at line 73 of file convolution.h.
| void CVD::convolveWithBox | ( | const BasicImage< T > & | I, |
| BasicImage< T > & | J, | ||
| ImageRef | hwin | ||
| ) |
convolves an image with a box of given size.
- Parameters:
-
I input image, modified in place hwin window size, this is half of the box size
Definition at line 151 of file convolution.h.
References CVD::assign_multiple(), CVD::SubImage< T >::data(), CVD::differences(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, CVD::ImageRef::y, and CVD::zeroPixels().
| void CVD::fast_nonmax | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier, | ||
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | max_corners | ||
| ) |
Perform non-maximal suppression on a set of FAST features.
This cleans up areas where there are multiple adjacent features, using a computed score function to leave only the 'best' features. This function is typically called immediately after a call to fast_corner_detect() (or one of its variants). This uses the scoring function given in the paper given in fast_corner_detect_9:
- Parameters:
-
im The image used to generate the FAST features corners The FAST features previously detected (e.g. by calling fast_corner_detect()) barrier The barrier used to calculate the score, which should be the same as that passed to fast_corner_detect() max_corners Vector to be filled with the new list of locally maximal corners.
| void CVD::fast_nonmax_with_scores | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< ImageRef, int > > & | max_corners | ||
| ) |
Perform non-maximal suppression on a set of FAST features, also returning the score for each remaining corner.
This function cleans up areas where there are multiple adjacent features, using a computed score function to leave only the 'best' features. This function is typically called immediately after a call to fast_corner_detect() (or one of its variants).
- Parameters:
-
im The image used to generate the FAST features corners The FAST features previously detected (e.g. by calling fast_corner_detect()) barrier The barrier used to calculate the score, which should be the same as that passed to fast_corner_detect() max_corners Vector to be filled with the new list of locally maximal corners, and their scores. non_maxcorners[i].firstgives the location andnon_maxcorners[i].secondgives the score (higher is better).
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_7 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 7 point FAST feature detection.
This is more like an edge detector. If you use this, please cite the paper given in fast_corner_detect_9
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_7 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 7 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_8 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 8 point FAST feature detection.
This is more like an edge detector. If you use this, please cite the paper given in fast_corner_detect_9
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_8 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 8 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_9 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 9 point FAST feature detection as described in: Machine Learning for High Speed Corner Detection, E.
Rosten and T. Drummond. Results show that this is both the fastest and the best of the detectors. If you use this in published work, please cite:
@inproceedings{rosten2006machine,
title = "Machine Learning for High Speed Corner Detection",
author = "Edward Rosten and Tom Drummond",
year = "2006",
month = "May",
booktitle = "9th European Conference on Computer Vision",
}
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_9 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 9 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_9_nonmax | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | max_corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform FAST-9 corner detection (see fast_corner_detect_9), with nonmaximal suppression (see fast_corner_score_9 and nonmax_suppression)
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of locally maximal corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_10 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 10 point FAST feature detection If you use this, please cite the paper given in fast_corner_detect.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_10 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 10 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_11 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 11 point FAST feature detection If you use this, please cite the paper given in fast_corner_detect_9.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_11 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 11 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::fast_corner_detect_12 | ( | const BasicImage< byte > & | im, |
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | barrier | ||
| ) |
Perform tree based 12 point FAST feature detection If you use this, please cite the paper given in fast_corner_detect_9.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Corner detection threshold
| void CVD::fast_corner_score_12 | ( | const SubImage< byte > & | i, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, | ||
| int | b, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | scores | ||
| ) |
Compute the 11 point score (as the maximum threshold at which the point will still be detected) for a std::vector of features.
- Parameters:
-
im The input image corners The resulting container of corner locations barrier Initial corner detection threshold. Using the same threshold as for corner detection will produce the quickest results, but any lower value (e.g. 0) will produce correct results.
| void CVD::haar1D | ( | It | from, |
| It | to | ||
| ) | [inline] |
computes the 1D Haar transform of a signal in place.
This version takes two iterators, and the data between them will be transformed. Will only work correctly on 2^N data points.
- Parameters:
-
from iterator pointing to the beginning of the data to iterator pointing to the end (after the last element)
Definition at line 58 of file haar.h.
Referenced by CVD::haar1D(), and CVD::haar2D().
| void CVD::inv_haar1D | ( | It | from, |
| It | to | ||
| ) | [inline] |
computes the inverse 1D Haar transform of a signal in place.
This version takes two iterators, and the data between them will be transformed. Will only work correctly on 2^N data points.
- Parameters:
-
from iterator pointing to the beginning of the data to iterator pointing to the end (after the last element)
Definition at line 71 of file haar.h.
Referenced by CVD::inv_haar1D().
| void CVD::haar1D | ( | It | from, |
| int | size | ||
| ) | [inline] |
computes the 1D Haar transform of a signal in place.
Will only work correctly on 2^N data points.
- Parameters:
-
from iterator pointing to the beginning of the data size number of data points, should be 2^N
Definition at line 83 of file haar.h.
References CVD::haar1D().
| void CVD::inv_haar1D | ( | It | from, |
| int | size | ||
| ) | [inline] |
computes the inverse 1D Haar transform of a signal in place.
Will only work correctly on 2^N data points.
- Parameters:
-
from iterator pointing to the beginning of the data size number of data points, should be 2^N
Definition at line 93 of file haar.h.
References CVD::inv_haar1D().
| void CVD::haar2D | ( | It | from, |
| const int | width, | ||
| const int | height, | ||
| int | stride = -1 |
||
| ) | [inline] |
computes the 2D Haar transform of a signal in place.
Works only with data with power of two dimensions, 2^N x 2^ M.
- Parameters:
-
from iterator pointing to the beginning of the data width columns of data, should be 2^N height rows of data, should be 2^M stride offset between rows, if negative will be set to width
Definition at line 105 of file haar.h.
References CVD::haar1D().
Referenced by CVD::haar2D().
| void CVD::haar2D | ( | SubImage< T > & | I | ) | [inline] |
computes the 2D Haar transform of an image in place.
Works only with images with power of two dimensions, 2^N x 2^ M.
- Parameters:
-
I image to be transformed
Definition at line 137 of file haar.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::data(), CVD::haar2D(), CVD::SubImage< T >::row_stride(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| void CVD::harrislike_corner_detect | ( | const SubImage< B > & | i, |
| C & | c, | ||
| unsigned int | N, | ||
| float | blur, | ||
| float | sigmas, | ||
| BasicImage< float > & | xx, | ||
| BasicImage< float > & | xy, | ||
| BasicImage< float > & | yy | ||
| ) |
Generic Harris corner detection function.
This can use any scoring metric and can store corners in any container. The images used to hold the intermediate results must be passed to this function.
- Parameters:
-
i Input image. c Container holding detected corners N Number of corners to detect blur Blur radius to use sigmas Number of sigmas to use in blur. xx Holds the result of blurred, squared X gradient. xy Holds the result of blurred, X times Y gradient. yy Holds the result of blurred, squared Y gradient.
Definition at line 81 of file harris_corner.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, CVD::ImageRef::y, and CVD::zeroBorders().
| void CVD::integral_image | ( | const SubImage< S > & | in, |
| SubImage< D > & | out | ||
| ) |
Compute an integral image.
In an integral image, pixel (x,y) is equal to the sum of all the pixels in the rectangle from (0,0) to (x,y) in the original image. and reallocation is not performed if b is unique and of the correct size.
- Parameters:
-
D The destination image pixel type S The source image pixel type in The source image. out The source image.
Definition at line 40 of file integral_image.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| Image<D> CVD::integral_image | ( | const BasicImage< S > & | from | ) |
Compute an integral image.
In an integral image, pixel (x,y) is equal to the sum of all the pixels in the rectangle from (0,0) to (x,y) in the original image. Type deduction is automatic, and D can not be specified. The following usage will work:
Image<byte> a; Image<int> b; ... b = integral_image(a);
Note that this is performed using lazy evaluation, so convertion happens on evaluation of assignment, and reallocation is not performed if b is unique and of the correct size.
- Parameters:
-
D The destination image pixel type S The source image pixel type from The source image.
- Returns:
- The integral image
| double CVD::interpolate_extremum | ( | double | d1, |
| double | d2, | ||
| double | d3 | ||
| ) |
Interploate a 1D local extremem by fitting a quadratic tho the three data points and interpolating.
The middle argument must be the most extreme, and the extremum position is returned relative to 0.
Arguments are checked for extremeness by means of assert.
- Parameters:
-
d1 Data point value for $x=-1$ d2 Data point value for $x=0$ d3 Data point value for $x=1$
- Returns:
- The $x$ coordinate of the extremum.
Definition at line 43 of file interpolate.h.
Referenced by CVD::interpolate_extremum().
| TooN::Vector<2> CVD::interpolate_extremum | ( | double | I__1__1, |
| double | I__1_0, | ||
| double | I__1_1, | ||
| double | I_0__1, | ||
| double | I_0_0, | ||
| double | I_0_1, | ||
| double | I_1__1, | ||
| double | I_1_0, | ||
| double | I_1_1 | ||
| ) |
Interpolate a 2D local maximum, by fitting a quadratic.
This is done by using using the 9 datapoints to compute the local Hessian using finite differences and finding the location where the gradient is zero.
Given the grid of pixels:
a b c d e f g h i
The centre pixel (e) must be the most extreme of all the pixels.
- Parameters:
-
I__1__1 Pixel $(-1, -1)$ relative to the centre (a) I__1_0 Pixel $(-1, 0)$ relative to the centre (b) I__1_1 Pixel $(-1, 1)$ relative to the centre (c) I_0__1 Pixel $( 0, -1)$ relative to the centre (d) I_0_0 Pixel $( 0, 0)$ relative to the centre (e) I_0_1 Pixel $( 0, 1)$ relative to the centre (f) I_1__1 Pixel $( 1, -1)$ relative to the centre (g) I_1_0 Pixel $( 1, 0)$ relative to the centre (h) I_1_1 Pixel $( 1, 1)$ relative to the centre (i)
- Returns:
- Location of the local extrema.
Definition at line 77 of file interpolate.h.
| TooN::Vector<2> CVD::interpolate_extremum | ( | const SubImage< I > & | i, |
| ImageRef | p | ||
| ) |
Interpolate a 2D local maximum, by fitting a quadratic.
- Parameters:
-
i Image in which to interpolate extremum p Point at which to interpolate extremum
- Returns:
- Location of local extremum in image coordinates
Definition at line 113 of file interpolate.h.
References CVD::interpolate_extremum(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::vec(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| std::pair<TooN::Vector<2>, double> CVD::interpolate_extremum_value | ( | double | I__1__1, |
| double | I__1_0, | ||
| double | I__1_1, | ||
| double | I_0__1, | ||
| double | I_0_0, | ||
| double | I_0_1, | ||
| double | I_1__1, | ||
| double | I_1_0, | ||
| double | I_1_1 | ||
| ) |
Interpolate a 2D local maximum, by fitting a quadratic.
This is done by using using the 9 datapoints to compute the local Hessian using finite differences and finding the location where the gradient is zero. This version returns also the value of the extremum.
Given the grid of pixels:
a b c d e f g h i
The centre pixel (e) must be the most extreme of all the pixels.
- Parameters:
-
I__1__1 Pixel $(-1, -1)$ relative to the centre (a) I__1_0 Pixel $(-1, 0)$ relative to the centre (b) I__1_1 Pixel $(-1, 1)$ relative to the centre (c) I_0__1 Pixel $( 0, -1)$ relative to the centre (d) I_0_0 Pixel $( 0, 0)$ relative to the centre (e) I_0_1 Pixel $( 0, 1)$ relative to the centre (f) I_1__1 Pixel $( 1, -1)$ relative to the centre (g) I_1_0 Pixel $( 1, 0)$ relative to the centre (h) I_1_1 Pixel $( 1, 1)$ relative to the centre (i)
- Returns:
- pair containing Location of the local extrema and the value
Definition at line 156 of file interpolate.h.
Referenced by CVD::interpolate_extremum_value().
| std::pair<TooN::Vector<2>, double> CVD::interpolate_extremum_value | ( | const SubImage< I > & | i, |
| ImageRef | p | ||
| ) |
Interpolate a 2D local maximum, by fitting a quadratic.
- Parameters:
-
i Image in which to interpolate extremum p Point at which to interpolate extremum
- Returns:
- pair containing Location of local extremum in image coordinates and the value of the extemum
Definition at line 193 of file interpolate.h.
References CVD::interpolate_extremum_value(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::vec(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| void CVD::morphology | ( | const SubImage< T > & | in, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | selem, | ||
| const Accumulator & | a_, | ||
| SubImage< T > & | out | ||
| ) |
Perform a morphological operation on the image.
At the edge of the image, the structuring element is cropped to the image boundary. This function is for homogenous structuring elements, so it is suitable for erosion, dialtion and etc, not hit-and-miss and so on.
For example:
Image<byte> image, eroded;
vector<ImageRef> structuring_element = getDisc(10);
...
morphology(image, structure_element, Erode<byte>(), eroded);
Morphology is performed efficiently using an incremental algorithm. As the structuring element is moved across the images, only pixels on it's edge are added and removed. Other morphological operators can be added by creating a class with the following methods:
template<class T> struct Operation { void insert(const T&); //Add a pixel void remove(const T&); //Remove a pixel void clear(const T&); //Remove all pixels T get(); //Get the current value. }
Grayscale erode could be implemented with a multiset to store and remove pixels. Get would simply return the first element in the multiset.
- Parameters:
-
in The source image. selem The structuring element. See e.g. getDisc() a_ The morphological operation to perform. See Morphology out The destination image.
Definition at line 76 of file morphology.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| Image<T> CVD::morphology | ( | const SubImage< T > & | in, |
| const std::vector< ImageRef > & | selem, | ||
| const Accumulator & | a_ | ||
| ) |
Perform a morphological operation on the image.
- Parameters:
-
in The source image. selem The structuring element. See e.g. getDisc() a_ The morphological operation to perform. See Morphology out The destination image.
| void CVD::nonmax_suppression_strict | ( | const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, |
| const std::vector< int > & | scores, | ||
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | nmax_corners | ||
| ) |
Perform nonmaximal suppression on a set of features, in a 3 by 3 window.
The test is strict: a point must be greater than its neighbours.
- Parameters:
-
corners The corner locations scores The corners' scores max_corners The locally maximal corners.
| void CVD::nonmax_suppression | ( | const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, |
| const std::vector< int > & | scores, | ||
| std::vector< ImageRef > & | nmax_corners | ||
| ) |
Perform nonmaximal suppression on a set of features, in a 3 by 3 window.
The test is non-strict: a point must be at least as large as its neighbours.
- Parameters:
-
corners The corner locations scores The corners' scores max_corners The locally maximal corners.
| void CVD::nonmax_suppression_with_scores | ( | const std::vector< ImageRef > & | corners, |
| const std::vector< int > & | socres, | ||
| std::vector< std::pair< ImageRef, int > > & | max_corners | ||
| ) |
Perform nonmaximal suppression on a set of features, in a 3 by 3 window.
Non strict.
- Parameters:
-
corners The corner locations scores The corners' scores max_corners The locally maximal corners, and their scores.
| Image<TooN::Matrix<2> > CVD::dense_tensor_vote_gradients | ( | const SubImage< C > & | image, |
| double | sigma, | ||
| double | ratio, | ||
| double | cutoff = 0.001, |
||
| unsigned int | num_divs = 4096 |
||
| ) |
This function performs tensor voting on the gradients of an image.
The voting is performed densely at each pixel, and the contribution of each pixel is scaled by its gradient magnitude. The kernel for voting is computed as follows. Consider that there is a point at 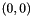 , with gradient normal
, with gradient normal 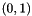 . This will make a contribution to the point
. This will make a contribution to the point 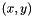 .
.
The arc-length, 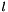 , of the arc passing through
, of the arc passing through 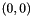 , tangent to the gradient at this point and also passing through
, tangent to the gradient at this point and also passing through 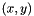 is:
is:
![\[ l = 2 r \theta \]](form_32.png)
Where
![\[ \theta = \tan^{-1}\frac{y}{x} \]](form_33.png)
and the radius of the arc, 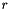 is:
is:
![\[ r = \frac{x^2 + y^2}{2y}. \]](form_35.png)
The scale of the contribution is:
![\[ s = e^{-\frac{l^2}{\sigma^2} - \kappa\frac{\sigma^2}{r^2}}. \]](form_36.png)
Note that this is achieved by scaling 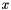 and
and 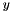 by
by 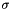 , so
, so 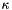 controls the kernel shape independent of the size. The complete tensor contribution is therefore:
controls the kernel shape independent of the size. The complete tensor contribution is therefore:
![\[ e^{-\frac{l^2}{\sigma^2} - \kappa\frac{\sigma^2}{r^2}} \left[ \begin{array}{c} \cos 2\theta\\ \sin 2\theta \end{array} \right] [ \cos 2\theta\ \ \sin 2\theta] \]](form_40.png)
- Parameters:
-
image The image on which to perform tensor voting sigma 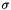
ratio 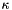
cutoff When 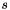 points drop below the cutoff, it is set to zero.
points drop below the cutoff, it is set to zero. num_divs The voting kernels are quantized by angle in to this many dicisions in the half-circle.
Definition at line 80 of file tensor_voting.h.
References CVD::BasicImage< T >::begin(), CVD::SubImage< T >::row_stride(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| void CVD::twoThirdsSample | ( | const SubImage< C > & | in, |
| SubImage< C > & | out | ||
| ) |
Subsamples an image to 2/3 of its size by averaging 3x3 blocks into 2x2 blocks.
- Parameters:
-
in input image out output image (must be out.size() == in.size()/3*2)
- Exceptions:
-
IncompatibleImageSizes if out does not have the correct dimensions.
Definition at line 47 of file vision.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::ImageRef::x, and CVD::ImageRef::y.
| Image<C> CVD::twoThirdsSample | ( | const SubImage< C > & | from | ) |
Subsamples an image by averaging 3x3 blocks in to 2x2 ones.
Note that this is performed using lazy evaluation, so subsampling happens on assignment, and memory allocation is not performed if unnecessary.
- Parameters:
-
from The image to convert from
- Returns:
- The converted image
| void CVD::halfSample | ( | const BasicImage< T > & | in, |
| BasicImage< T > & | out | ||
| ) |
subsamples an image to half its size by averaging 2x2 pixel blocks
- Parameters:
-
in input image out output image, must have the right dimensions versus input image
- Exceptions:
-
IncompatibleImageSizes if out does not have half the dimensions of in
Definition at line 118 of file vision.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::data(), CVD::SubImage< T >::size(), CVD::SubImage< T >::totalsize(), and CVD::ImageRef::x.
Referenced by CVD::halfSample().
| Image<T> CVD::halfSample | ( | const BasicImage< T > & | in | ) | [inline] |
subsamples an image to half its size by averaging 2x2 pixel blocks
- Parameters:
-
in input image
- Returns:
- The output image
- Exceptions:
-
IncompatibleImageSizes if out does not have half the dimensions of in
Definition at line 149 of file vision.h.
References CVD::halfSample(), and CVD::SubImage< T >::size().
| Image<T> CVD::halfSample | ( | Image< T > | in, |
| unsigned int | octaves | ||
| ) | [inline] |
subsamples an image repeatedly by half its size by averaging 2x2 pixel blocks.
This version will not create a copy for 0 octaves because it receives already an Image and will reuse the data.
- Parameters:
-
in input image octaves number of halfsamplings
- Returns:
- The output image
- Exceptions:
-
IncompatibleImageSizes if out does not have half the dimensions of in
Definition at line 165 of file vision.h.
References CVD::halfSample().
| void CVD::threshold | ( | BasicImage< T > & | im, |
| const T & | minimum, | ||
| const T & | hi | ||
| ) |
thresholds an image by setting all pixel values below a minimum to 0 and all values above to a given maximum
- Parameters:
-
im input image changed in place minimum threshold value hi maximum value for values above the threshold
Definition at line 178 of file vision.h.
References CVD::BasicImage< T >::begin(), and CVD::BasicImage< T >::end().
| void CVD::stats | ( | const BasicImage< T > & | im, |
| T & | mean, | ||
| T & | stddev | ||
| ) |
computes mean and stddev of intensities in an image.
These are computed for each component of the pixel type, therefore the output are two pixels with mean and stddev for each component.
- Parameters:
-
im input image mean pixel element containing the mean of intensities in the image for each component stddev pixel element containing the standard deviation for each component
Definition at line 198 of file vision.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::data(), and CVD::SubImage< T >::totalsize().
| void CVD::gradient | ( | const BasicImage< S > & | im, |
| BasicImage< T > & | out | ||
| ) |
computes the gradient image from an image.
The gradient image contains two components per pixel holding the x and y components of the gradient.
- Parameters:
-
im input image out output image, must have the same dimensions as input image
- Exceptions:
-
IncompatibleImageSizes if out does not have same dimensions as im
Definition at line 260 of file vision.h.
References CVD::SubImage< T >::size().
 1.7.4
1.7.4